Despite being a preventable disease, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death and hospitalization, particularly in children and older adults. According to the World Health Organization, pneumonia accounts for 14% of all deaths in children under the age of 5 and killed 740,180 children in 2019 alone. The American Thoracic Society also reports that pneumonia is one of the top reasons for hospitalization in children and the most common cause of hospital admissions in US adults other than childbirth.
Symptoms of pneumonia can include a persistent, non-stop cough, trouble breathing, chest pain, and fever. These symptoms can be frightening, but there are steps we can take to lower the risk of developing pneumonia. Huawei Dong, M.D., a pulmonology and critical care medicine professor at the University of California, Irvine School of Medicine and pulmonologist at UCI Health, states that inhaling any type of irritant, such as smoke or chemicals, can weaken our natural defenses against germs and increase our risk of pneumonia. This is particularly true for smoking and vaping, which can cause significant harm to our lung health.
In conclusion, pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening lung infection that affects millions of people every year. While anyone can develop pneumonia, children and older adults are at the greatest risk. To reduce the risk of developing pneumonia, it is important to avoid inhaling harmful chemicals, such as smoke and chemicals from vaping. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of pneumonia, it is essential to seek medical care promptly to receive the necessary treatment and prevent any potential complications.
1) Everything You Need to Know About Pneumonia

Pneumonia and bronchitis are two respiratory illnesses that can cause similar symptoms, making it difficult for individuals to differentiate between the two. However, it is important to know the difference as the treatments for each condition vary.
According to Dr. Fady Youssef, a pulmonologist and critical care specialist, pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that requires medical attention. On the other hand, bronchitis is inflammation of the airways, which can be caused by an infection or other factors.
Dr. Dong, a physician specializing in respiratory illnesses, adds that pneumonia is caused by inhaling germs such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening, depending on the type of infection and the individual's health.
In conclusion, it is important to seek medical attention when experiencing symptoms of pneumonia or bronchitis to accurately diagnose the condition and receive the appropriate treatment.
2) The Dangers of Pneumonia: Understanding its Impact as a Major Cause of Mortality
When it comes to vital organs in the body, the heart and lungs hold a special place. Any infection or ailment that affects either of these organs can quickly become life-threatening. Pneumonia, in particular, has been a leading cause of death in the United States for many years, ranking among the top 10 causes. However, the recent COVID-19 pandemic has seen it rise to become the third leading cause of death, surpassed only by heart disease and cancer.
Pneumonia is a serious condition that can lead to fatal complications, such as respiratory failure and sepsis, making it particularly dangerous. Time is of the essence in treating pneumonia, as severe cases can lead to death within hours, as the victim drowns in the fluids flooding their lungs.
In Honduras, the threat of pneumonia is being addressed through a national, integrated community child care program. This program trains community volunteers to monitor children's growth, provide health education, and treat pneumonia and diarrhea. By providing early intervention and treatment, the program aims to reduce the fatal consequences of pneumonia in children.
In conclusion, pneumonia is a serious and life-threatening condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. While it has been a leading cause of death for many years, its rise to the third leading cause of death due to the COVID-19 pandemic highlights the urgent need for increased awareness and action. By working together to address this threat, we can help reduce the devastating impact of pneumonia on our communities.
3) Older Adults and children are more susceptible to infections
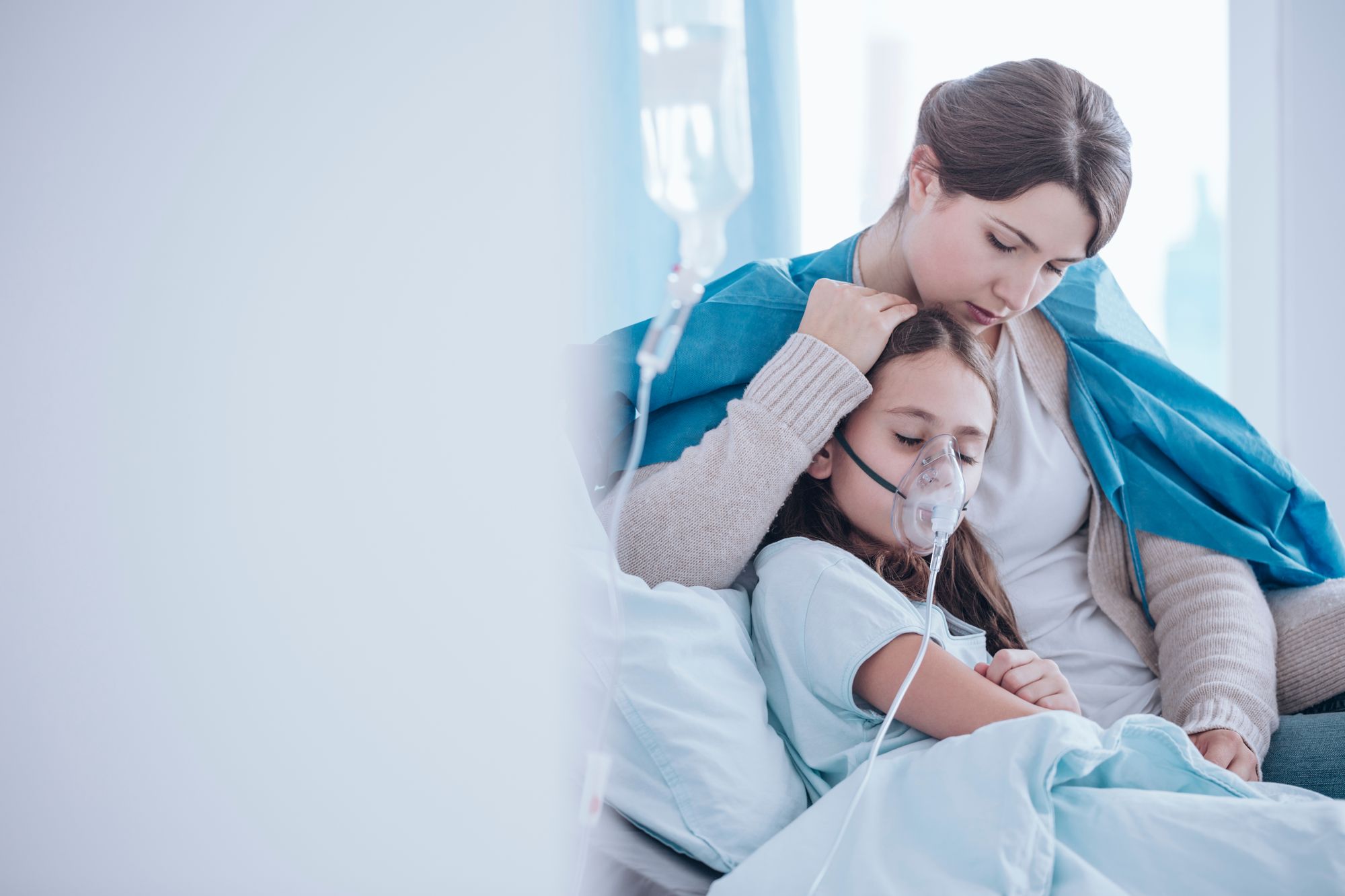

Dr. Dong explains, "The immune system of children is not yet fully mature until they reach the age of 6-7. With age, the immune system weakens, making both young children and adults over 65 more vulnerable to infections. However, as children continue to age and are exposed to various germs and vaccines, their immune system will become stronger. On the other hand, as people enter their golden years, the natural defense mechanisms of their body start to decline, making them more susceptible to illnesses such as pneumonia, especially if they have additional health issues."
4) The Slow Recovery from Pneumonia: Understanding the Reasons Behind It
Dr. Youssef explains, "The recovery process from pneumonia can vary depending on the severity of the infection. For mild cases, patients typically start feeling better within 5 to 7 days and return to their normal state within 2 to 4 weeks. However, in severe cases, the recovery may take longer and the lungs may take up to 4 to 6 weeks to fully heal, as seen on a chest X-Ray. During the infection, the lungs become filled with germs, fluid, and debris from damaged cells, and even if the germs are killed, it can take time for the body to clear this material. In severe cases, pneumonia can even lead to permanent lung damage."
Dr. Dong adds, "The long recovery period from pneumonia is also due to the fact that the infection can cause a significant degree of deconditioning. This can make it difficult for the patient to return to their normal level of activity, even after they start feeling better."
5) Antibiotic Resistance in Pneumonia: A Growing Concern
Antibiotic resistance is a rapidly growing problem that is affecting people all over the world. According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2019, there were approximately 30,300 cases of invasive pneumococcal disease, and over 30% of these cases were caused by pneumococcal bacteria that were resistant to one or more antibiotics. This is a concerning trend that highlights the need for action to address this issue.
Pneumonia is a severe respiratory infection that can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It is a serious condition that can lead to severe complications if left untreated. The use of antibiotics is the standard treatment for pneumonia, but if the bacteria causing the infection are resistant to antibiotics, then alternative treatment options may need to be considered.
According to Dr. Youssef, if you are treated with oral antibiotics and your symptoms do not start to improve within 2-3 days or worsen, you need to seek medical attention. In some cases, alternate oral antibiotics or intravenous antibiotics may be necessary to effectively treat the infection.
Dr. Dong also emphasizes the importance of seeing your doctor if you are not improving despite taking antibiotics. He says that further testing may be needed to determine if a different antibiotic may work better or if there are other medical reasons for the lack of improvement. He also stresses the importance of finishing your entire antibiotic prescription, as early stoppage is a well-known cause of more antibiotic resistance.
In conclusion, the growing problem of antibiotic resistance is a serious concern that requires immediate attention. Pneumonia is one of the many infections that can be caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and it is essential to be vigilant about seeking medical attention if your symptoms do not start to improve or worsen while taking antibiotics. By working together, we can help to reduce the threat of antibiotic resistance and ensure that effective treatment options are available for those who need them.
6) Avoid These Mistakes When Dealing with Pneumonia

Listen to your body and see a doctor if your symptoms persist or worsen, says Dr. Dong. Scans like x-rays or CTs can diagnose pneumonia. To help slow the spread of germs, stay home and avoid social gatherings until you feel better.
For symptom relief, Dr. Youssef suggests taking rest, staying hydrated, using over-the-counter medications, and avoiding smoking, both first and second hand.
7) Indicators of Pneumonia: What to Look For

Dr. Dong warns of common symptoms: "Cough, fever, fatigue, and in severe cases, shortness of breath, chest pain, and confusion are all indications of pneumonia." Dr. Youssef adds to the list: "Fever, chills, cough, fatigue, low energy, poor appetite, muscle aches, shortness of breath, chest tightness."
According to the Mayo Clinic, the severity of pneumonia symptoms can vary and may include chest pain, confusion, phlegm-producing cough, fatigue, fever, chills, low body temperature, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and shortness of breath. In older adults and those with weakened immune systems, a lower body temperature may also be a sign of pneumonia.