If you're struggling to trim unwanted belly fat, your eating habits could be the key. While exercise is crucial for fat loss, achieving a toned midsection requires a mindful approach to your diet. While there's no magic solution or one-size-fits-all approach to losing belly fat, addressing harmful eating habits can greatly impact your journey to a slimmer waistline.
The impact of unhealthy foods and eating habits on belly fat accumulation is significant. Foods high in refined sugars, processed ingredients, and trans fats are particularly problematic as they contribute to increased visceral (abdominal) fat. According to Harvard Medical School, visceral belly fat is associated with numerous health risks, including metabolic conditions, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and even breast cancer and the need for gallbladder surgery in women.
To discover the primary eating habits undermining your waistline, we consulted Destini Moody, RDN, CSSD, LD, a registered dietitian and sports dietitian associated with Garage Gym Reviews. Moody unveils the ten most detrimental eating habits that might impede your progress and maintain stubborn belly fat. By confronting these habits directly, you can pave the path toward a leaner, healthier version of yourself. Continue reading to find out more.
1) Eating While Distracted
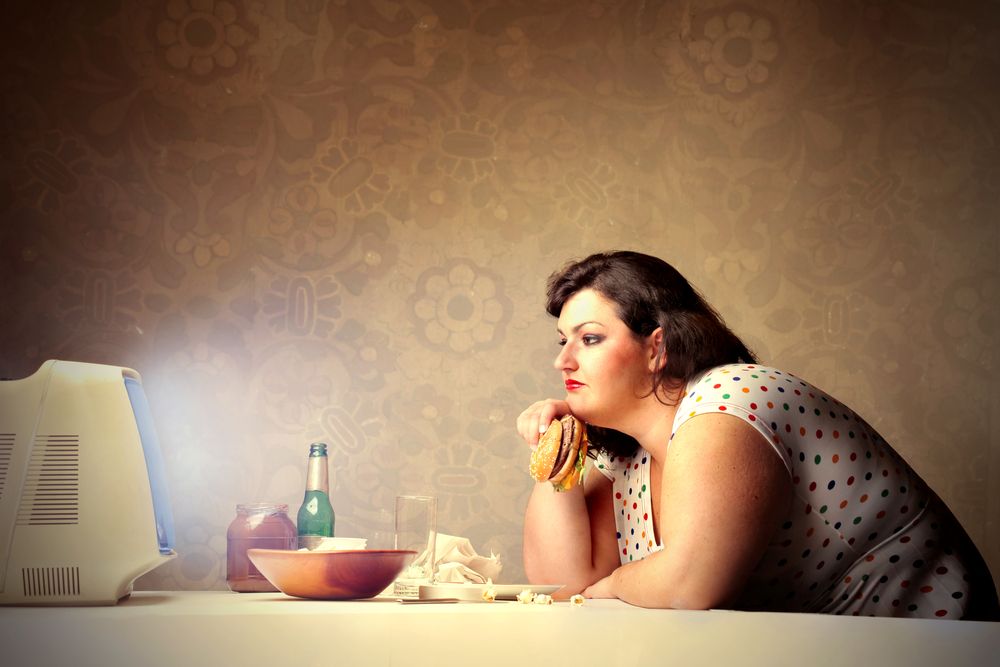

Engaging in distractions like TV or phone scrolling during meals often leads to unknowingly consuming larger portions. This harmful habit can trigger overeating and contribute to weight gain, particularly around the midsection. According to a study in the Journal of Health Psychology, individuals who ate while distracted consumed five times more than those who focused solely on their meal.
Moody explains, "When you're not mindful of eating, your brain may fail to signal fullness to your stomach because you're not fully tuned into the eating experience. This can result in consuming more than intended, ultimately leading to an accumulation of belly fat."
2) Drinking Too Much Alcohol
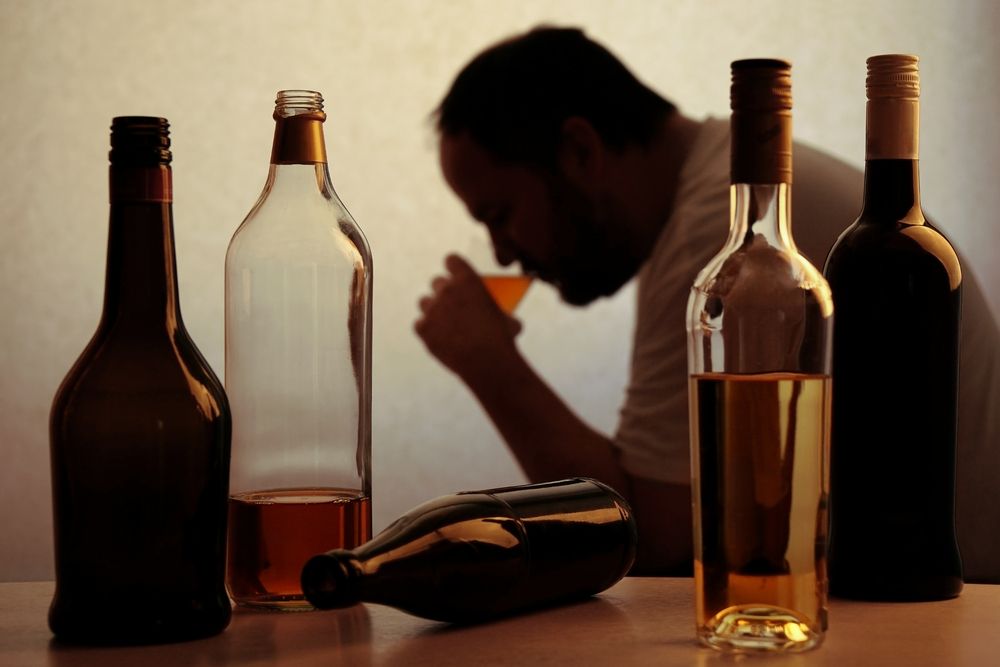

Alcoholic drinks are packed with empty calories, and excessive consumption can contribute to the accumulation of belly fat. When you consume alcohol, your body prioritizes metabolizing it over burning fat. "Alcohol, especially wine and beer with added calories from sugar and wheat, contains a significant amount of calories," Moody points out. "Moreover, it can disrupt your metabolism." Studies indicate that excessive alcohol intake can disrupt certain hormones responsible for fat-burning and hunger regulation.
3) Not Staying Hydrated

Dehydration can occasionally masquerade as hunger, prompting unnecessary snacking and overeating. Cultivate a routine of drinking water consistently throughout the day to nourish your body and regulate your appetite. "Often, we mistake thirst for hunger, which can result in snacking or overeating when all we really need is some water. Therefore, maintaining hydration levels can assist in managing those hunger signals," advises Moody.
4) Overeating High-Calorie Healthy Foods

Though nutrient-rich foods are vital for a balanced diet, it's crucial to monitor your portion sizes. Foods like nuts, avocados, and olive oil boast ample nutrients but are also calorie-dense. "Nuts, seeds, and avocados offer an array of antioxidants, nutrients, and beneficial unsaturated fats. However, they can pack quite a caloric punch," explains Moody. "For instance, just a quarter cup of walnuts can contain around 200 calories. That's why consuming trail mix or mixed nuts directly from the bag can lead to significant weight gain, despite their healthful qualities."
5) Eating Out Too Often

Meals served at restaurants frequently contain added fats and sugars, which are primary contributors to abdominal fat. If you're considering dining out, choosing to cook at home instead can offer you greater command over ingredients and serving sizes, consequently reducing your calorie consumption.
Moody warns, "Indulging in excessive dining out not only strains your budget but can also expand your waistline. Restaurants and fast-food chains often provide portions that far surpass what's necessary, aiming to provide a perception of value for your money. In addition to excessive levels of sodium and saturated fat, these meals frequently incorporate added sugars, which contribute to chronic inflammation and weight gain."
6) Not Eating Enough Fruits and Veggies

Fruits and vegetables are abundant sources of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, crucial for maintaining a nutritious and balanced diet. Insufficient intake of these nutrient-rich foods can lead to cravings for less healthy alternatives. Moody elaborates, "Since our high school health classes, we've been aware of the health benefits of fruits and vegetables. Yet, they also boast fiber and antioxidants that aid in slowing digestion, managing appetite, and alleviating chronic inflammation. Additionally, vegetables can enhance meal volume without substantially increasing calorie intake, thereby helping to reduce overall calorie consumption."
7) Skipping Meals

As per the University of Louisville, forgoing meals can disturb your metabolism and trigger overeating later in the day. Thankfully, organizing and readying meals ahead of time can assist in adhering to your weight loss objectives and sustaining a regular eating routine.
Moody elucidates, "The issue with skipping meals is that your body's hunger hormones tend to compensate later. If you've ever missed breakfast and felt those hunger pangs hit hard in the late afternoon, you're likely familiar with this phenomenon. Such an imbalance can lead to excessive snacking, particularly late at night."
8) Not Eating Enough Protein

Protein stands out as the most satisfying macronutrient, and insufficient intake may trigger cravings for unhealthy snacks, which can lead to abdominal fat accumulation. Moody elaborates, "Beyond promoting a greater sense of fullness, protein aids in preserving muscle mass. Enhanced muscle mass can boost metabolism, resulting in more calories burned even at rest. Moreover, the process of digesting protein consumes more calories compared to digesting carbohydrates or fat."
9) Relying on Supplements
While dietary supplements can offer benefits, relying solely on them for nutrition isn't a sustainable or practical approach. Instead, they should complement a balanced diet. "The purpose of supplements is to supplement an already healthy diet," advises Moody. "Opting for a morning greens powder in lieu of fresh vegetables or relying on a multivitamin instead of improving your overall diet isn't advisable." Consuming nutritious foods provides essential phytonutrients and fiber that supplements cannot replace. These components play a crucial role in managing belly fat and inflammation levels. It's crucial to prioritize whole foods for health and weight management and use supplements to address specific nutritional gaps, rather than relying on them exclusively."
10) Mindless Snacking

Mindlessly snacking throughout the day, without considering portion sizes or nutritional value, can result in excessive calorie intake. To encourage mindful eating, the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health suggests adhering to structured meal and snack times, enjoying each bite, and staying attuned to your body's hunger and fullness signals. These tactics facilitate more deliberate decision-making, foster a healthier dietary equilibrium, and help prevent the accumulation of belly fat.

