Although healthcare workers are appreciated, no one wants to make unnecessary trips to the emergency room. By adopting good health habits and making positive lifestyle choices, you can reduce your chances of avoidable hospital stays. Dr. Tomi Mitchell, a board-certified family physician with Holistic Wellness Strategies, shares her tips for staying healthy. Read on to learn more and ensure the health of yourself and those around you. And don't miss these sure signs you've already had COVID-19.
1) How to Avoid Unnecessary Hospital Visits

According to Dr. Mitchell, hospitalization should be the last option for treating ailments. Hospital admission is usually required for people who are already severely ill and require intensive medical care. Even though hospitalization is sometimes necessary to save lives, it is not a guaranteed cure-all. Patients must receive follow-up care to ensure a complete recovery after being discharged from the hospital. This may involve ongoing specialist treatment or therapy to manage symptoms.
The road to recovery can be lengthy and challenging for many people, but it's important to remain optimistic. With dedicated medical care and support, patients can make a full recovery and return to their daily routine. Dr. Mitchell will provide case studies of typical scenarios in which someone might end up in the hospital to avoid such situations.
2) Meet Theo, Age 55
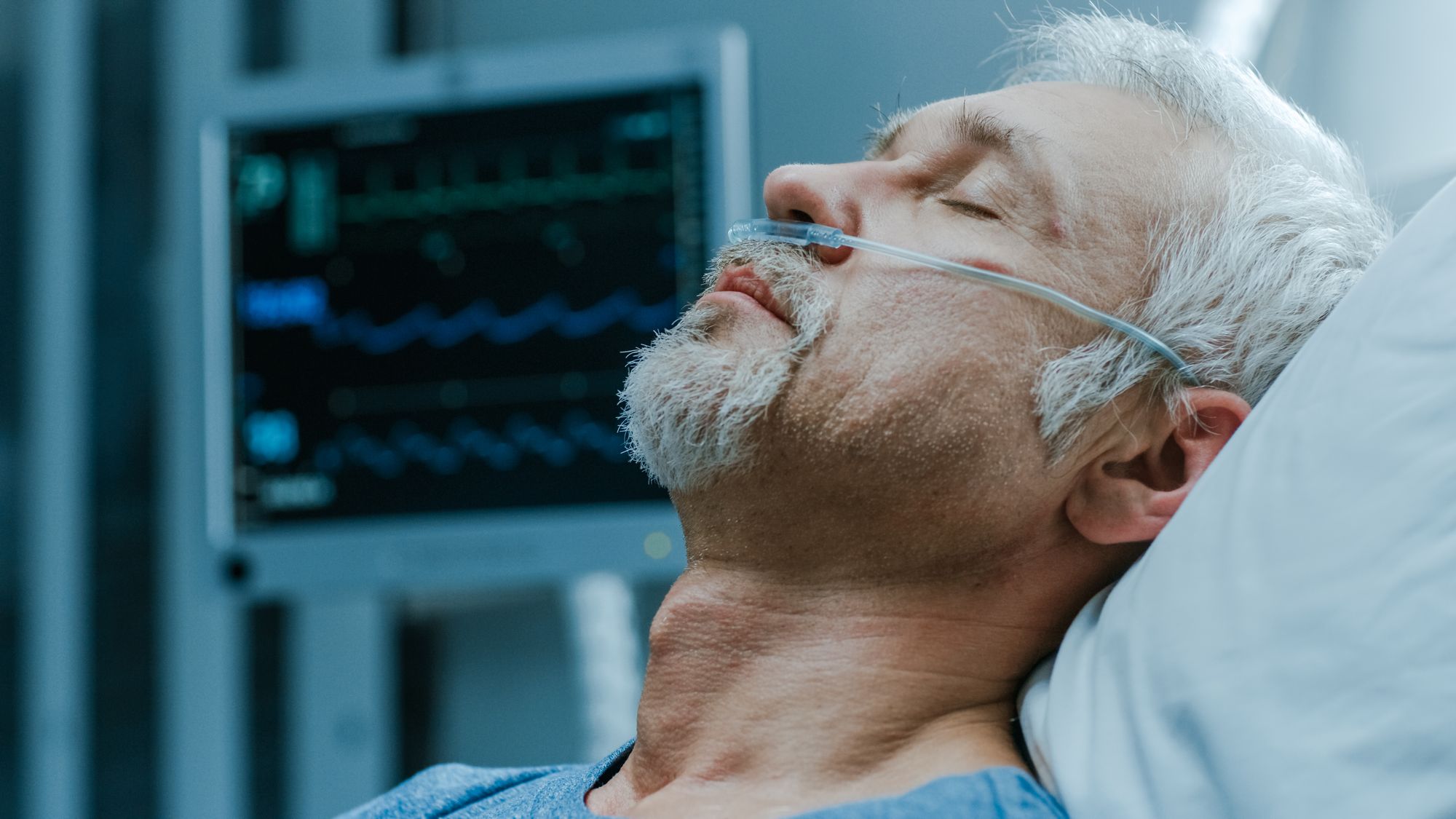
Dr. Mitchell discusses the case of Theo, who arrived at a busy downtown hospital with severe symptoms, including stomach pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and dry skin and mouth. After further questioning, it was discovered that he had undiagnosed diabetes and was suffering from a potentially fatal condition called Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA occurs when blood sugar is too high and the body cannot produce enough insulin. Early symptoms of DKA include frequent urination, thirst, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Without prompt treatment, DKA can lead to organ damage, diabetic coma, and death
Dr. Mitchell uses Theo's case to emphasize the importance of regular medical checkups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of hospitalization. Theo had several risk factors, including obesity, smoking, and a history of pancreatitis and GERD. He also had a poor attitude towards preventive care and neglected his health until it became an emergency. By prioritizing regular checkups, healthy eating habits, exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive drinking, individuals can decrease their likelihood of developing chronic conditions that may require hospitalization.
3) Heavy for his Height

According to Dr. Mitchell, Theo's medical obesity increased his risk of hospitalization. Regular physical activity could have helped Theo to reduce the risk of several chronic health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer, which are some of the leading causes of hospitalization in the United States. In fact, obese adults are nearly twice as likely to be hospitalized as healthy-weight adults. The risk of hospitalization is higher for obese individuals for several reasons, including developing chronic health conditions that require hospital care, difficulty moving, and the complication of medical treatments. For instance, obese patients may be less responsive to medications or more likely to experience side effects from medicines.
Fortunately, there are several measures that people can take to reduce their risk of hospitalization due to obesity. Firstly, they can maintain a healthy weight by following a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity. Secondly, they can manage chronic health conditions with the help of their healthcare provider. Lastly, they should undergo regular checkups and screenings to detect potential problems early. By taking these steps, people can significantly reduce their risk of being hospitalized due to obesity.
4) Age

Dr. Mitchell stresses that age is an unchangeable risk factor, affecting everyone. Older adults have a higher likelihood of hospitalization due to various factors. As we age, our immune system weakens, making us more susceptible to diseases and infections. Chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis, are also more prevalent in older adults, leading to hospitalization. Social isolation, caused by factors like retirement and loss of a spouse, can also contribute to poor health outcomes. Additionally, cognitive decline can make it challenging to manage healthcare needs effectively.
Fortunately, there are steps that older adults can take to reduce their risk of hospitalization. Maintaining social connections, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet can help keep the body and mind healthy. Regular medical checkups can also detect and address health issues before they become severe. By taking care of themselves, older adults can decrease their risk of hospitalization and maintain their quality of life.
5) Lack of Regular Preventative Screening Tests Detected in Patient
Dr. Mitchell stresses the importance of not skipping preventative screening tests. These tests play a crucial role in detecting potentially life-threatening conditions like diabetes at an early stage. Moreover, screening exams can help identify risk factors for other diseases like hypertension, which is a risk factor for heart disease and stroke. These exams are a critical component of maintaining good health. However, many people tend to skip these tests due to their busy schedules or lack of health insurance, which can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment. Thus, it is crucial to prioritize preventative screenings and find healthcare providers who offer these services to avoid adverse health outcomes.
6) Use of Alcohol

According to Dr. Mitchell, "Alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on your health and increase your risk of hospitalization for various reasons." Firstly, alcohol consumption can lead to dehydration, which can result in severe health conditions. Secondly, it can interfere with the regulation of blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of hospitalization in individuals with diabetes. Thirdly, alcohol use can elevate the likelihood of injuries such as falls and car accidents.
If you are concerned about your risk of being hospitalized due to alcohol consumption, there are some actions you can take. The first step is to limit your consumption to no more than one drink per day. Secondly, ensure that you drink plenty of water to stay hydrated when consuming alcohol. Lastly, avoid drinking before engaging in activities that could be risky, such as driving. Taking these precautions can significantly lower your chances of being hospitalized due to alcohol consumption.
7) Smoker

According to Dr. Mitchell, "Smoking not only increases the risk of severe health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and cancer, but it can also increase the likelihood of hospitalization." Research has shown that smokers are more likely to be hospitalized for various conditions, such as respiratory illnesses, infections, and pregnancy complications. Moreover, those who smoke heavily or have been smoking for many years face even higher risks.
Furthermore, smoking is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes, a condition that occurs when the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels properly. Smokers are more than twice as likely as nonsmokers to develop type 2 diabetes, and those who smoke heavily or for an extended period are at higher risk. If you are a smoker, it is crucial to quit smoking as soon as possible to safeguard your health. Consult with your physician to learn about ways to quit smoking effectively.

