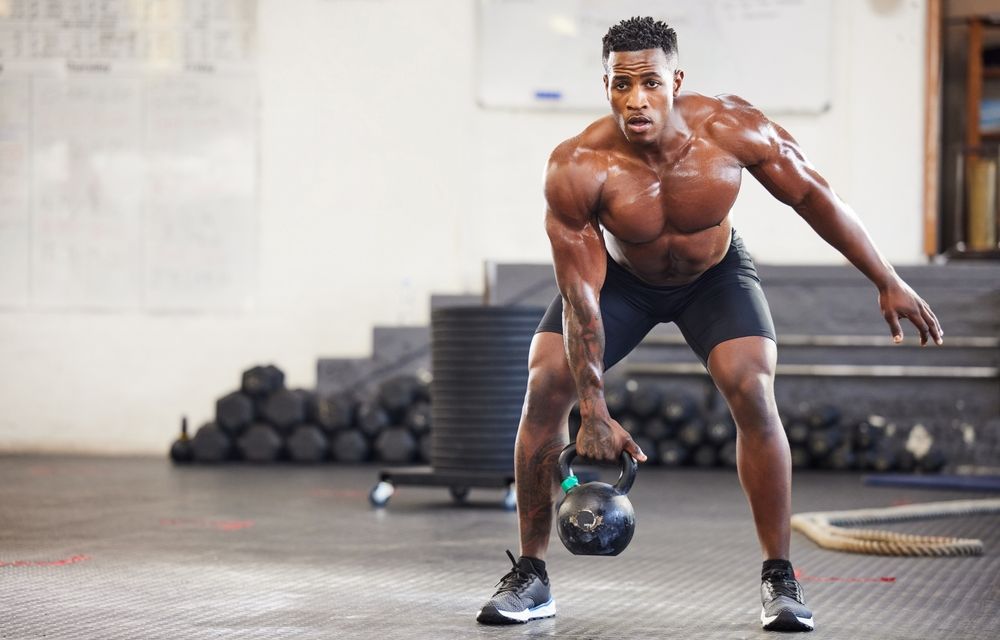
Supersets involve performing two consecutive exercises with minimal rest in between, effectively maintaining a heightened heart rate and maximizing fat-burning potential. These exercises often target different or opposing muscle groups, such as pairing a chest exercise with a back exercise. Whether your goal is weight loss, overall fitness improvement, or a blend of both, incorporating these five top superset workouts can be highly beneficial.
The advantages of utilizing supersets are manifold. Firstly, they elevate workout intensity, fostering increased muscle engagement and potential gains in strength, muscle size, and body composition. Additionally, supersets offer a time-efficient workout solution, allowing for more work to be accomplished in less time compared to traditional sets with rest intervals. Furthermore, they contribute to improved cardiovascular fitness through the continuous nature of the exercises, thereby enhancing overall conditioning and optimizing weight loss potential. Lastly, supersets inject variety into workout routines, staving off boredom and ensuring continued interest and engagement.
Please continue reading to discover some of my preferred superset workouts tailored for weight loss, which I regularly incorporate into my training sessions with personal clients and athletes. When time is limited and ambitious goals await, harnessing the power of supersets proves to be one of the most effective tools in your fitness toolkit.
1) Upper-body Superset
For a potent upper-body superset, combine an upper-body push exercise (such as bench press or shoulder press variations) with an upper-body pull (like rows, pull-ups, or lat pulldowns). To maximize your workout effectiveness, I suggest aligning vertical exercises with horizontal ones. For example, pair a bench press variation with a bent-over row, and vice versa for vertical presses and pulldowns. This strategic pairing ensures comprehensive muscle engagement and optimizes training efficiency.
Incline Dumbbell Bench Presses
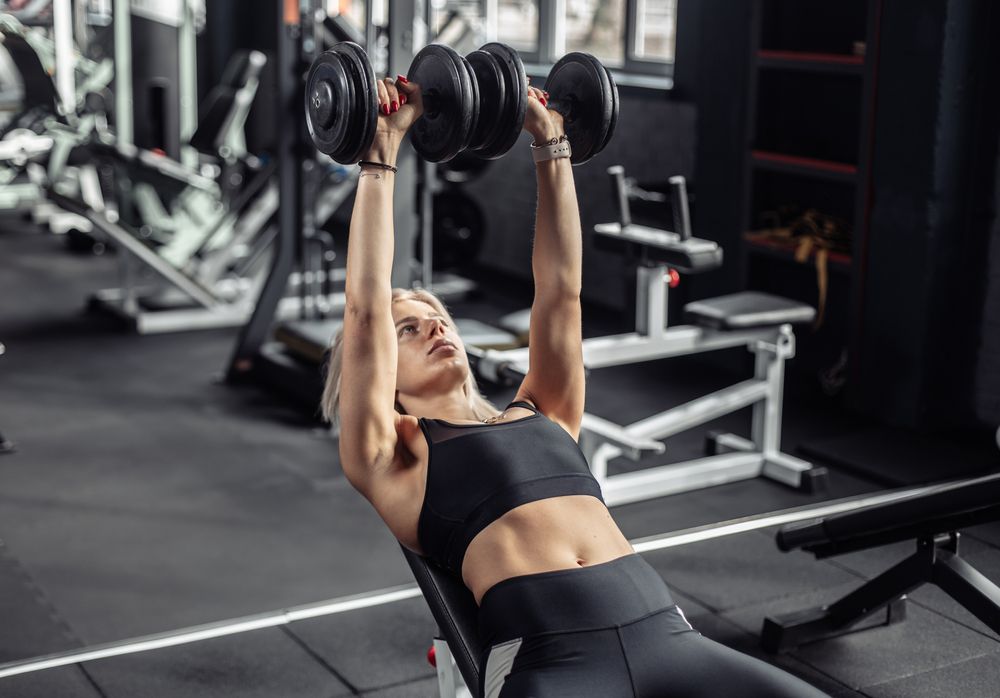

The incline dumbbell bench press is a dynamic exercise designed to target and fortify your upper chest, front delts, and triceps. By incorporating dumbbells, this movement amplifies muscle engagement, necessitating stabilization with each repetition. Renowned for its efficacy, this exercise consistently yields impressive results, enhancing upper-body strength and fostering substantial muscle growth.
To execute the incline dumbbell bench press effectively, begin by sitting on a slightly inclined bench. Grasp a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder level, ensuring your palms face forward. Maintain a stable position with your feet planted on the floor and your back firmly against the bench, engaging your core muscles. Exhale as you push the dumbbells upward, extend your arms without locking your elbows, and pause momentarily at the movement's peak. Inhale as you lower the dumbbells back down to shoulder level, maintaining controlled movement throughout.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of eight to 15 repetitions of the incline dumbbell bench press. Then, seamlessly transition into the incline chest-supported row set to further maximize your upper-body workout.
Incline Chest-supported Rows
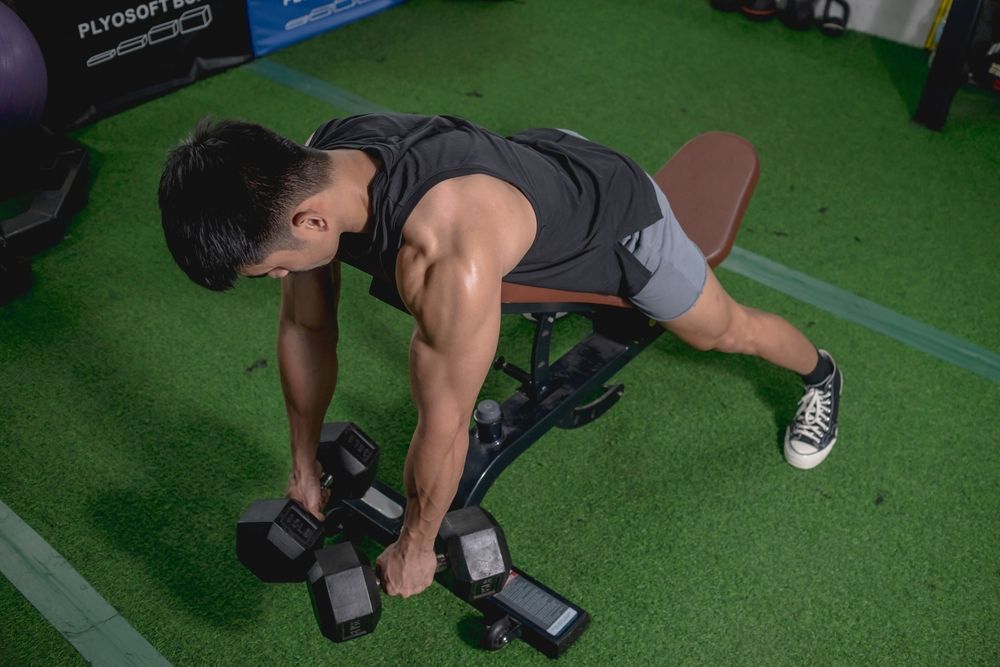

The incline chest-supported dumbbell row is a highly effective exercise for targeting the upper back muscles, particularly the lats, rhomboids, and rear deltoids. By positioning your chest on an incline bench, you stabilize your body and isolate the intended muscles, minimizing the risk of momentum-driven cheating. This setup facilitates a full range of motion and optimal muscle engagement, leading to improved posture, strength, and muscular balance in the upper body.
To perform the exercise, lie face down on an incline bench. Hold a dumbbell in each hand with your palms facing inward. Pull the weights toward your ribcage while maintaining firm contact between your chest and the bench, exhaling as you do so. Concentrate on squeezing your shoulder blades together at the top of the movement. Inhale as you lower the dumbbells back down in a controlled manner.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of eight to 15 repetitions of the incline chest-supported dumbbell row, with 90 seconds of rest between supersets.
2) Lower-body Superset
Prepare for an impactful lower-body superset that promises results! This dynamic combination pairs a hip hinge exercise, focusing on your glutes and hamstrings, with a lower-body push exercise that activates your quads. By blending these movements, you'll optimize muscle engagement and sculpt your lower body comprehensively.
Dumbbell Hip Thrusts
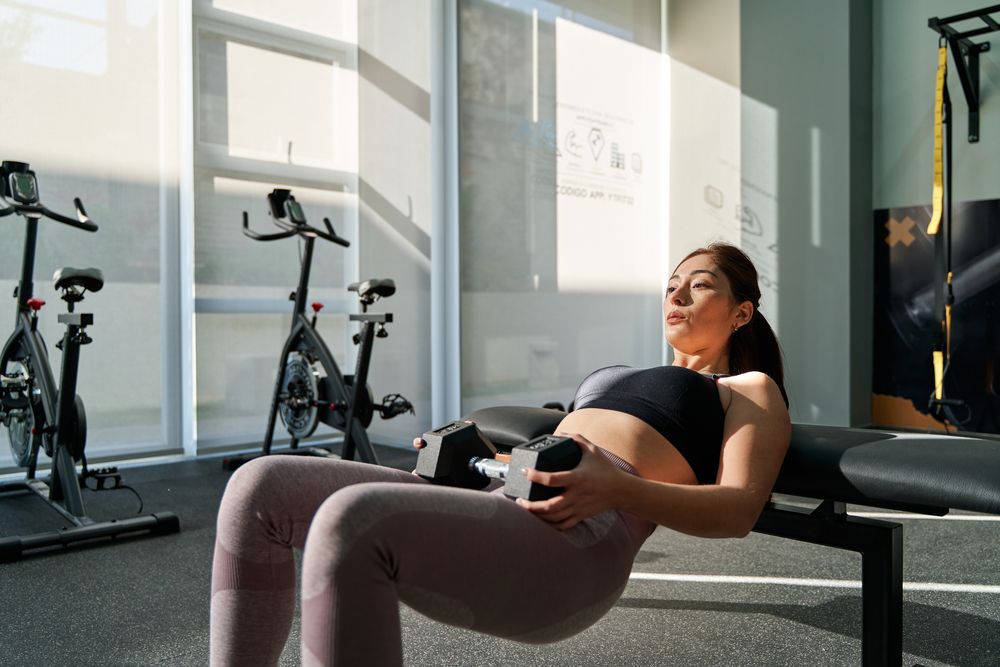

The dumbbell hip thrust primarily targets your glutes and lower back, with the hamstrings contributing to positional strength. It ranks among the top exercises, alongside glute bridges, for amplifying muscle size and strength in your hips. Incorporating this movement into your routine can yield substantial gains in power and definition in this vital muscle group.
To perform the exercise, start by positioning yourself on the floor with your upper back against a bench and a dumbbell resting on your hips. Bend your knees and firmly plant your feet on the ground, ensuring they are hip-width apart. Drive through your heels to push your hips up until your body forms a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. Squeeze your glutes at the top of the movement, then lower your hips with control.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of six to 12 repetitions of the dumbbell hip thrust. Then, seamlessly transition into the box step-up set to further enhance your lower-body workout.
Box Step-ups
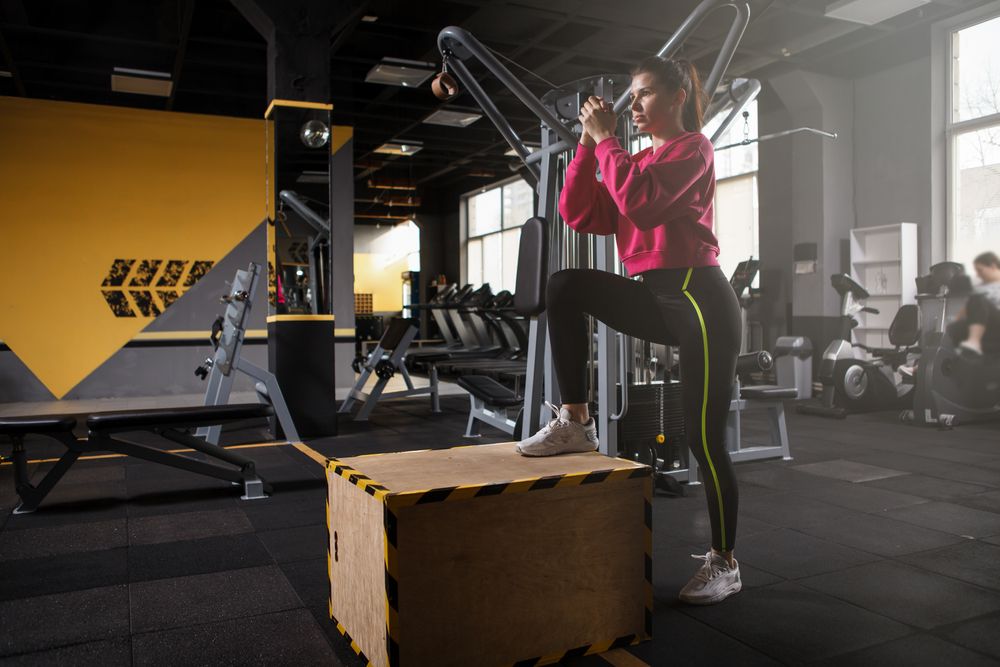

Box step-ups are exceptional for targeting lower-body muscles, especially the quadriceps. When incorporated into a superset, they introduce a cardiovascular challenge while promoting muscular endurance and strength. Furthermore, the unilateral nature of step-ups helps rectify any muscle imbalances and enhances overall functional fitness.
To perform the exercise, start by standing in front of a sturdy box or bench with your feet hip-width apart. Step onto the box with your right foot, pressing through it to propel your body upward. Bring your left foot up to meet your right foot on top of the box, then lower yourself back down with control. Alternate legs for the desired number of repetitions, ensuring to keep your chest and core engaged throughout the movement. Adjust the box height according to your fitness level.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of six to 12 repetitions per side of box step-ups, with 90 seconds of rest between supersets.
3) Upper Push, Lower Pull Superset
Employing an upper push, lower pull superset approach combines exercises that emphasize the chest and shoulders for the upper body with movements targeting the hamstrings and glutes (posterior chain) for the lower body. This method optimizes muscle engagement and time efficiency by alternating between upper and lower-body exercises, which allows for longer rest periods. Consequently, you can lift heavier weights for more repetitions, maximizing workout effectiveness.
Single-Arm Dumbbell Push Presses
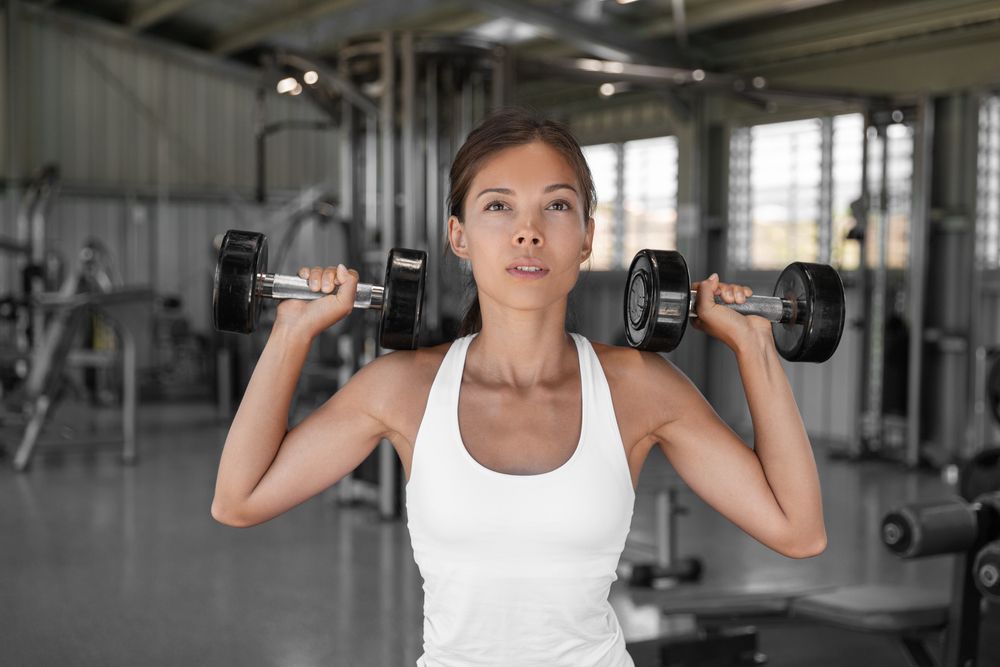

The dumbbell push press is a dynamic exercise that boosts overall power while fostering strength and muscle growth in the shoulders and triceps. By engaging your lower body to drive the dumbbell upward and completing the movement with a press, you achieve a comprehensive full-body training effect, making it ideal for weight loss workouts. Opting for the single-arm variation enhances stability through increased muscle recruitment and addresses any existing asymmetries, promoting a more balanced physique.
To perform the exercise, start by holding a dumbbell at shoulder height in one hand, with your elbow bent and palm facing inward. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, engage your core, and lower into a slight dip by bending your knees and hips. Next, explosively extend your legs and press the dumbbell overhead, utilizing momentum to assist the press. Lower the dumbbell back to the starting position under control.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of six to 12 repetitions per side of the dumbbell push press. Then, seamlessly transition into the single-leg dumbbell RDL set to further enhance your lower-body workout.
Single-Leg Dumbbell RDL
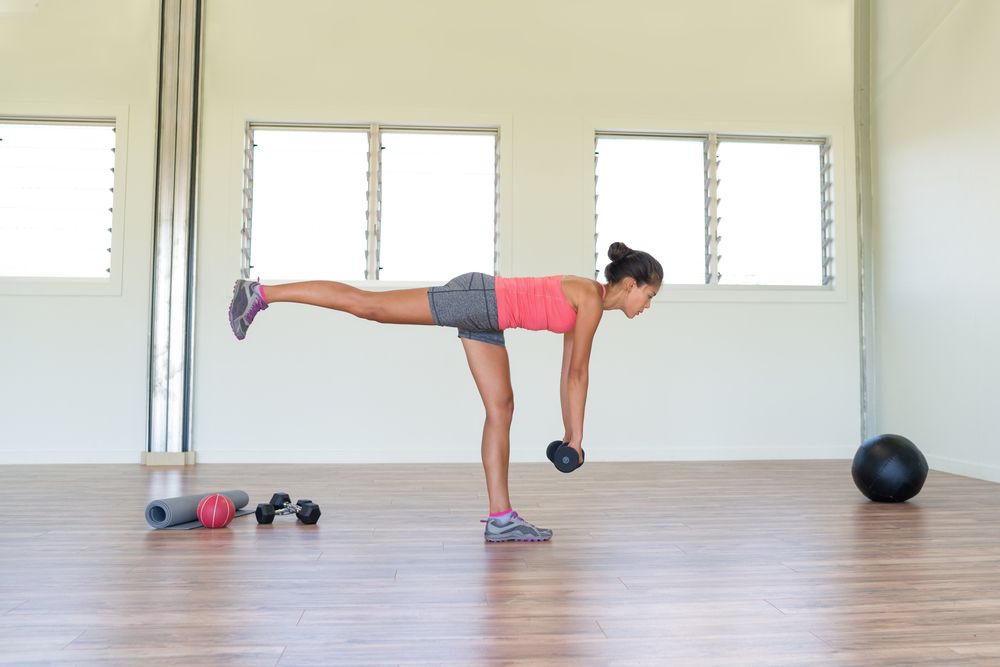

The single-leg dumbbell Romanian deadlift (RDL) stands out as a premier exercise choice, offering a multitude of benefits. Notably, it enhances balance and stability by isolating each leg, presenting a formidable challenge that addresses muscle imbalances effectively. This exercise zeroes in on key posterior chain muscles such as the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back, fostering strength and muscle development. Its unilateral nature contributes to improved functional strength and mobility, translating into enhanced performance in both everyday activities and sports.
To perform the exercise, begin by standing with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in one hand. Shift your weight to one leg while maintaining a slight knee bend, simultaneously hinging forward at the hips and extending the opposite leg behind you for balance. Lower the dumbbell toward the ground, ensuring to keep your back straight and hips level throughout the movement. Pause when parallel to the ground, then engage your hamstring and glute to return to the starting position.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of six to 12 repetitions per side of the single-leg dumbbell Romanian deadlift, with 90 seconds of rest between supersets.
4) Lower Push, Upper Pull Superset
Pairing lower-body push exercises with upper-body pull exercises in a superset is a strategic tactic in strength training that capitalizes on efficiency and effectiveness. By alternating between movements that target different muscle groups, such as squats or lunges for the lower body and rows or pull-ups for the upper body, you optimize muscle recruitment and stimulate overall muscle growth. This dynamic combination not only saves time but also enhances muscular balance and coordination, ultimately leading to strength gains throughout the body.
Back Squats
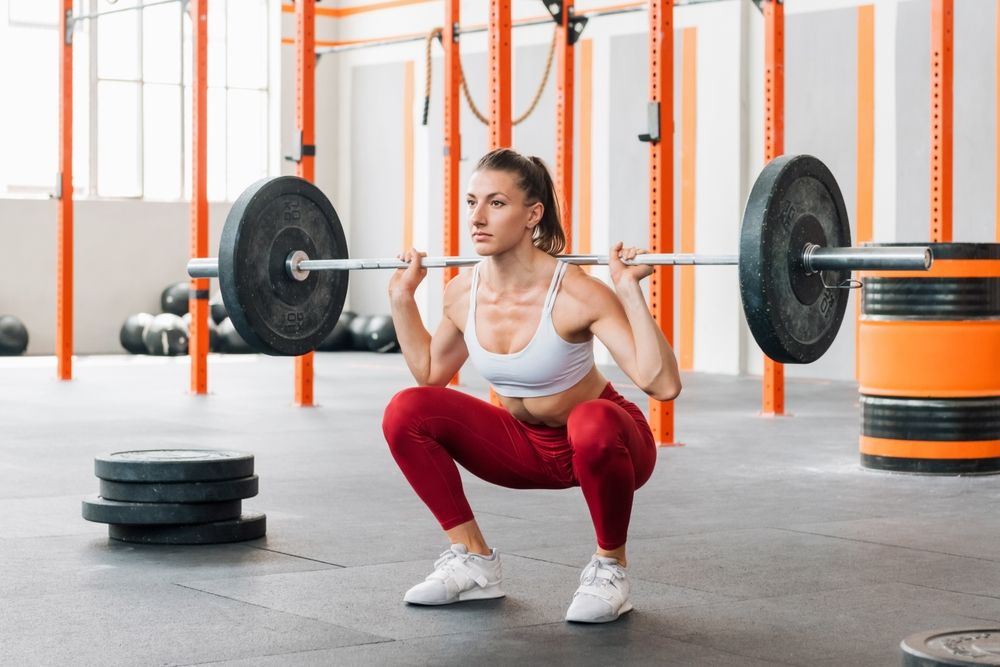

The back squat, revered as the pinnacle of lower-body push exercises, plays a vital role in cultivating lower-body strength, size, and mobility. By engaging your quads and glutes, it promotes lean muscle development, thereby enhancing your performance in the weight room and functional strength for everyday activities.
To perform the exercise, load your desired weight onto a barbell and position your hands just outside shoulder width on the racked barbell. Step under the bar, squeeze your traps, and rest the barbell on your upper back. Once set, step back from the squat rack, ensuring your feet are firmly planted hip-width apart. Brace your core, bend your knees, and descend into a squat, aiming to reach a 90-degree angle. Drive through your feet to stand back up, completing the repetition. Repeat for the desired number of reps before safely reracking the barbell between sets.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of eight to 12 repetitions of the back squat. Following this, seamlessly transition into the lat pulldown exercise.
If equipment or space limitations prevent you from performing back squats, feel free to substitute them with goblet squats, lunges, or step-ups.
Lat Pulldowns
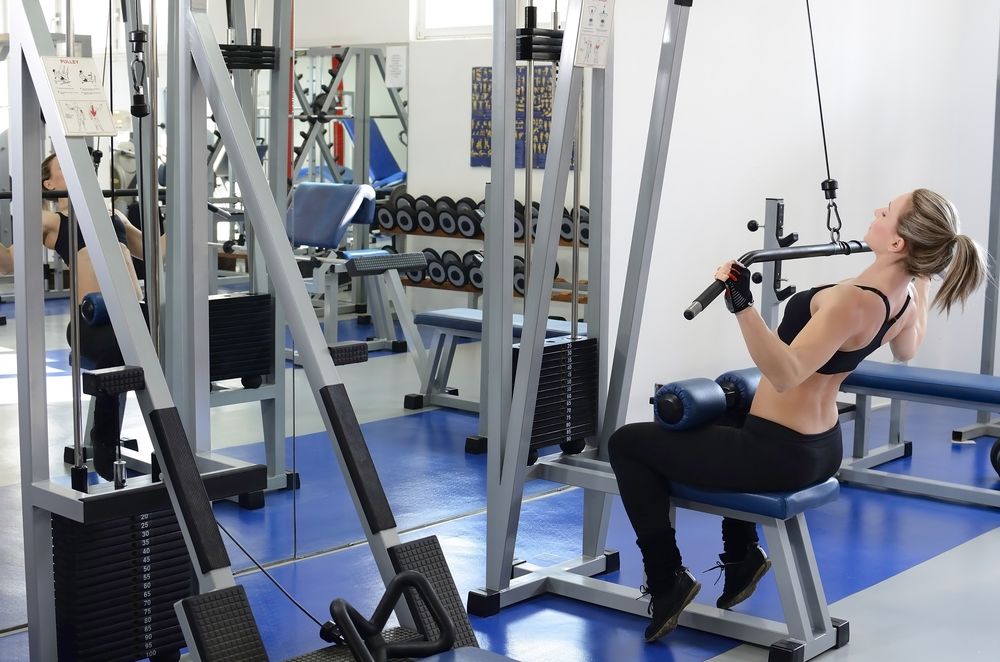

The lat pulldown stands out as the ultimate exercise for targeting the vertical muscle fibers of your upper and mid-back, enabling a higher volume compared to pull-ups or chin-ups. This exercise engages your lats, traps, and rhomboids, promoting significant upper-body strength and muscle development.
To perform the lat pulldown, start by gripping the attachment with your preferred grip width—whether overhand, underhand, or mixed. Securely sit down and place your knees underneath the pad, if available. Pull the bar down until it's beneath your chin, maintaining an upright posture with shoulders and chest up, and squeeze your lats. Slowly raise the bar back to the starting position, then repeat the movement for the desired number of repetitions.
For optimal results, aim to complete three to four sets of 15 to 20 repetitions of the lat pulldown, with 90 seconds of rest between supersets.
5) Full-body Superset
Prepare to ignite your metabolism and elevate both your heart rate and muscle engagement with this dynamic full-body superset. Get ready to feel the burn in your muscles and experience a surge in metabolic activity.
One of my favorite combinations is the kettlebell thruster paired with a bent-over row during a Romanian deadlift (RDL). This powerful duo isn't just about targeting isolated muscles; it's an approach that effectively engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Anticipate a significant impact on muscle growth, strength, and endurance, ensuring every rep counts towards your fitness goals.
In this workout, you'll follow a superset interval format. Alternate between 30 seconds of exercise and 30 seconds of rest for a total of 10 to 14 rounds. Perform kettlebell thrusters during even-numbered rounds and dumbbell Romanian deadlifts with a row during odd-numbered rounds. Get ready to push your limits and achieve remarkable results!
Kettlebell Thrusters
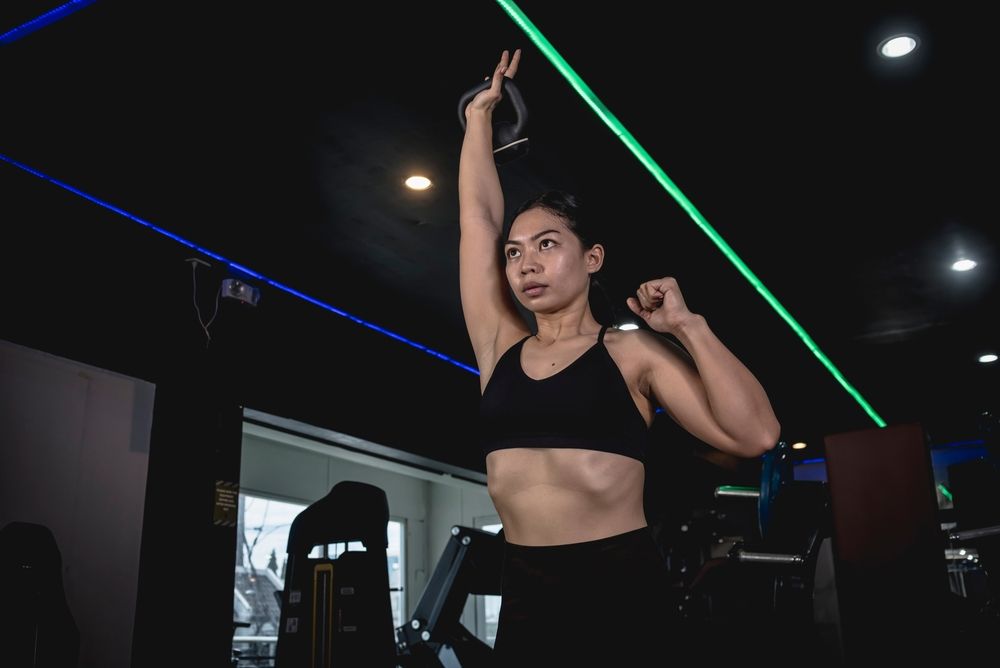

The kettlebell thruster is an excellent choice for inclusion in a superset due to its compound nature, which engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously. By combining a squat and an overhead press into one seamless movement, this exercise maximizes efficiency, intensity, and functional strength while also providing cardiovascular benefits.
To perform the exercise, start by grasping a kettlebell with an overhand grip at shoulder level, holding it in the front rack position. Position your feet shoulder-width apart. Descend into a squat while maintaining a straight back and keeping your core engaged. As you rise from the squat, press the kettlebell overhead, fully extending your arms. Lower the kettlebell back to shoulder height as you descend into the next squat repetition. Ensure smooth and controlled transitions throughout the movement.
Dumbbell RDLs to Rows
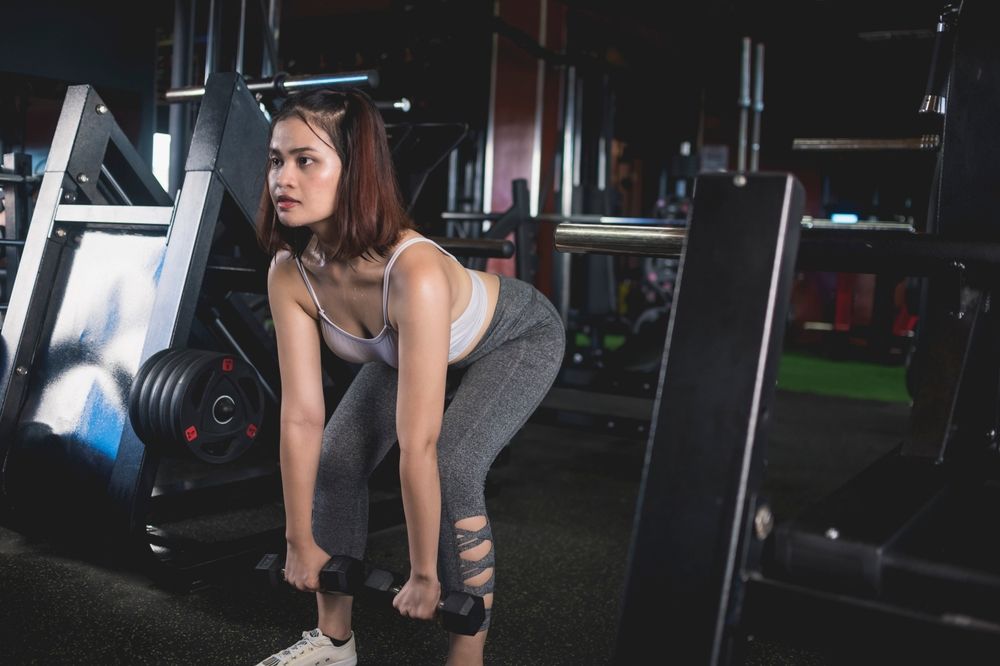
This dynamic combination is sure to ignite your posterior chain, targeting everything from your head to your hamstrings! The dumbbell Romanian deadlift to row seamlessly integrates the lower-body focus of a Romanian deadlift, targeting your hamstrings, glutes, and lower back, with the upper-body engagement of a bent-over row, enhancing strength and size gains in your lats, upper back, and core.
To perform the exercise, hold dumbbells in front of your thighs with a neutral grip and your feet hip-width apart. Hinge at your hips while keeping your back flat and knees slightly bent, lowering the dumbbells toward the ground to feel a stretch in your hamstrings. From the Romanian deadlift position, pull the dumbbells up toward your chest by squeezing your shoulder blades and bending your elbows, performing a row. Finally, extend your hips forward to return to the starting position.

